Pain is a complex and subjective experience that can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the importance of pain assessment is crucial for healthcare providers, as it serves as the foundation for effective treatment and management strategies. Pain assessment not only helps in identifying the intensity and nature of a patient’s pain but also provides insights into its underlying causes.
By accurately assessing pain, healthcare professionals can tailor interventions that address the specific needs of each patient, ultimately leading to improved outcomes. Moreover, pain assessment plays a vital role in fostering communication between patients and healthcare providers. It empowers patients to express their experiences and feelings regarding pain, which can often be difficult to articulate.
This dialogue is essential for building trust and rapport, allowing healthcare professionals to gain a deeper understanding of the patient’s condition. In this way, pain assessment becomes a collaborative process, where both parties work together to develop an effective pain management plan that aligns with the patient’s goals and preferences.
Key Takeaways
- Pain assessment is crucial for understanding and addressing a patient’s discomfort and improving their overall well-being.
- Effective treatment relies on accurate pain assessment to tailor interventions and monitor progress.
- Various tools, such as numerical rating scales and visual analog scales, are used to assess different aspects of pain.
- Proper pain assessment can lead to improved patient outcomes, including better pain management and overall satisfaction with care.
- Challenges in pain assessment include subjective nature of pain, cultural differences, and communication barriers, which healthcare professionals must navigate.
The Role of Pain Assessment in Effective Treatment
Effective treatment hinges on a thorough understanding of a patient’s pain experience. Pain assessment serves as a critical tool in this process, guiding healthcare providers in selecting appropriate interventions. By evaluating the type, location, intensity, and duration of pain, clinicians can identify potential underlying conditions and tailor their treatment approaches accordingly.
For instance, acute pain may require different management strategies compared to chronic pain, which often necessitates a more comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach. Furthermore, ongoing pain assessment allows for the monitoring of treatment efficacy. As patients undergo various interventions, regular evaluations can help determine whether the chosen strategies are effective or if adjustments are needed.
This dynamic process ensures that treatment remains responsive to the patient’s evolving needs and circumstances. By prioritizing pain assessment, healthcare providers can enhance the overall effectiveness of treatment plans, leading to better patient satisfaction and improved health outcomes.
Types of Pain Assessment Tools

A variety of pain assessment tools are available to assist healthcare professionals in evaluating pain effectively. These tools can be broadly categorized into self-report measures, observational tools, and physiological measures. Self-report measures are often considered the gold standard in pain assessment, as they rely on the patient’s subjective experience.
Common examples include numerical rating scales (NRS), visual analog scales (VAS), and standardized questionnaires such as the McGill Pain Questionnaire. These tools allow patients to quantify their pain levels and describe their experiences in detail. On the other hand, observational tools are particularly useful for assessing pain in individuals who may have difficulty communicating their experiences, such as young children or patients with cognitive impairments.
These tools often involve observing behavioral indicators of pain, such as facial expressions, body language, and vocalizations. Physiological measures, including heart rate and blood pressure monitoring, can also provide valuable insights into a patient’s pain experience. By utilizing a combination of these assessment tools, healthcare providers can gain a comprehensive understanding of a patient’s pain and develop targeted interventions.
The Impact of Pain Assessment on Patient Outcomes
| Pain Assessment Metric | Impact on Patient Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Frequency of Pain Assessment | Higher frequency of pain assessment leads to better pain management and improved patient satisfaction. |
| Use of Pain Scales | Using pain scales helps in accurately measuring and documenting pain, leading to better pain management and improved patient outcomes. |
| Timely Pain Assessment | Timely pain assessment allows for prompt intervention and better pain control, leading to improved patient comfort and satisfaction. |
| Comprehensive Pain Assessment | Comprehensive pain assessment helps in identifying underlying causes of pain, leading to better treatment outcomes and improved patient well-being. |
The impact of effective pain assessment on patient outcomes cannot be overstated. Research has consistently shown that accurate pain evaluation leads to improved management strategies, which in turn enhance patients’ overall well-being. When healthcare providers take the time to assess pain thoroughly, they are better equipped to address the specific needs of their patients.
This personalized approach not only alleviates suffering but also fosters a sense of empowerment among patients, as they feel heard and understood. Additionally, effective pain assessment can lead to reduced healthcare costs by minimizing unnecessary interventions and hospitalizations. When pain is accurately assessed and managed from the outset, patients are less likely to experience complications or exacerbations that require more intensive treatment.
This proactive approach not only benefits individual patients but also contributes to the overall efficiency of healthcare systems. By prioritizing pain assessment, healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes while simultaneously optimizing resource utilization.
The Challenges of Pain Assessment
Despite its importance, pain assessment is fraught with challenges that can hinder its effectiveness. One significant challenge is the inherent subjectivity of pain itself; what one person experiences as severe discomfort may be perceived as mild by another. This variability complicates the process of establishing standardized assessment protocols that can be universally applied across diverse patient populations.
Additionally, cultural differences can influence how individuals express and interpret pain, further complicating assessments. Another challenge lies in the limitations of existing assessment tools. While self-report measures are invaluable, they may not always capture the full complexity of a patient’s experience.
For instance, some patients may underreport their pain due to fear of stigma or concerns about being perceived as “complaining.” Conversely, others may exaggerate their symptoms for various reasons. These discrepancies highlight the need for healthcare professionals to employ a multifaceted approach to pain assessment that considers both subjective reports and objective observations.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals in Pain Assessment
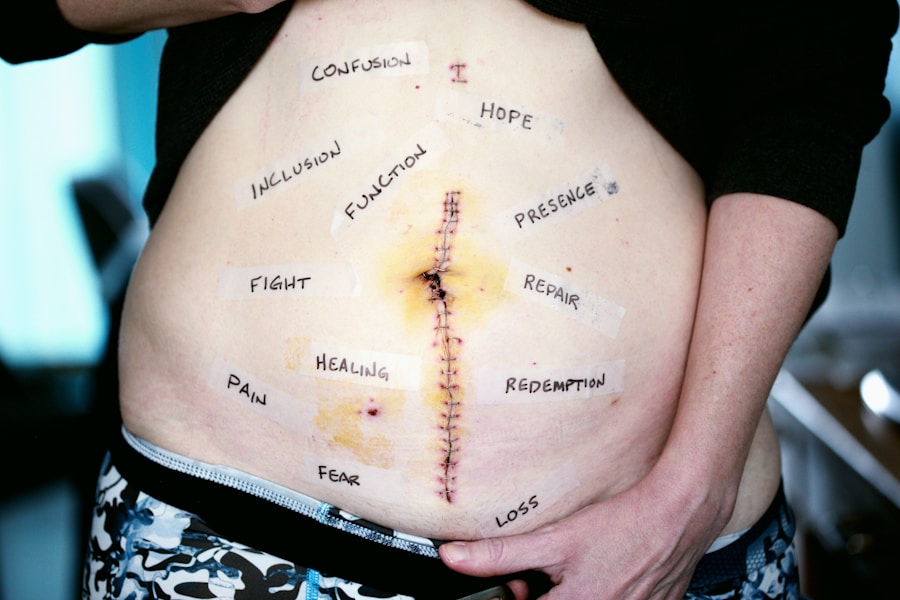
Healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in the pain assessment process. Their expertise and training equip them with the skills necessary to evaluate pain effectively and implement appropriate interventions. Physicians, nurses, physical therapists, and other allied health professionals must work collaboratively to ensure comprehensive assessments that address all aspects of a patient’s experience.
This interdisciplinary approach not only enhances the accuracy of assessments but also promotes holistic care. Moreover, healthcare professionals must remain vigilant in their efforts to stay informed about advancements in pain assessment methodologies and tools. Continuous education and training are essential for maintaining competency in this area, as new research findings and technologies emerge regularly.
By prioritizing ongoing professional development, healthcare providers can enhance their ability to assess pain accurately and implement evidence-based practices that improve patient outcomes.
Best Practices for Pain Assessment
Implementing best practices for pain assessment is essential for optimizing patient care. One key practice is to establish a routine for regular pain evaluations during patient encounters. This ensures that pain is consistently monitored and addressed throughout the course of treatment.
Additionally, healthcare providers should encourage open communication with patients about their pain experiences, fostering an environment where patients feel comfortable discussing their symptoms without fear of judgment. Another best practice involves utilizing a combination of assessment tools tailored to each patient’s unique circumstances. By employing both self-report measures and observational techniques, healthcare professionals can gain a more comprehensive understanding of a patient’s pain experience.
Furthermore, it is crucial to document assessments thoroughly in medical records to facilitate continuity of care and enable other providers to access relevant information when needed.
The Future of Pain Assessment in Healthcare
The future of pain assessment in healthcare holds great promise as advancements in technology and research continue to evolve. Innovations such as wearable devices and telehealth platforms are beginning to transform how pain is assessed and managed. These technologies offer real-time monitoring capabilities that allow healthcare providers to track patients’ pain levels remotely, enabling timely interventions when necessary.
Additionally, ongoing research into the neurobiology of pain is likely to yield new insights that could inform more effective assessment tools and treatment strategies. As our understanding of pain mechanisms deepens, healthcare professionals will be better equipped to develop personalized approaches that address the unique needs of each patient. Ultimately, the future of pain assessment will likely be characterized by a more integrated and patient-centered approach that prioritizes collaboration between patients and providers in managing this complex experience.
When it comes to pain assessment, it is crucial to consider various factors that may influence a patient’s experience. One related article that delves into the importance of thorough assessment is A Beginner’s Guide to Transcripted Interviews. Just as in interviews, where detailed questioning and active listening are essential for gathering accurate information, healthcare professionals must also employ similar techniques when assessing a patient’s pain levels. By understanding the nuances of pain assessment, healthcare providers can better tailor treatment plans to meet the individual needs of each patient.
FAQs
What is pain assessment?
Pain assessment is the process of evaluating a person’s pain intensity, location, quality, and other characteristics in order to determine the most effective treatment and management strategies.
Why is pain assessment important?
Pain assessment is important because it helps healthcare providers understand the nature and severity of a person’s pain, which is crucial for developing an appropriate treatment plan and ensuring the best possible outcomes for the patient.
What are the common methods used for pain assessment?
Common methods used for pain assessment include self-reporting by the patient, visual analog scales, numerical rating scales, and behavioral observation for non-verbal patients.
Who can perform pain assessment?
Pain assessment can be performed by healthcare professionals such as doctors, nurses, physical therapists, and other trained personnel who are familiar with pain assessment tools and techniques.
What are the challenges in pain assessment?
Challenges in pain assessment include the subjective nature of pain, cultural and language barriers, cognitive impairment in some patients, and the inability of non-verbal patients to communicate their pain.
How often should pain assessment be conducted?
The frequency of pain assessment depends on the individual patient’s condition and the type of pain they are experiencing. In general, pain assessment should be conducted regularly, especially in patients with chronic pain or those undergoing treatment for acute pain.